AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) is the main plasma protein produced by egg yolk bags, intestinal and liver tracts during fetal life. AFP expression in adults is often associated with hepatoma or teratoma. However, the persistence of AFP hereditary can also be found in individuals without clear pathology.
Protein is considered a serum fetus albumin partner, and AFP gene and albumin are present in the tandem in the same transcription orientation in chromosome 4. AFP is found in the form of monomers, damp, and trimeric. AFP can also tie copper ions, nickel ions, fatty acids and bilirubin. You can also know more about AFP antibodies-online via https://www.bosterbio.com/anti-alpha-1-fetoprotein-picoband-trade-antibody-a00522-boster.html.
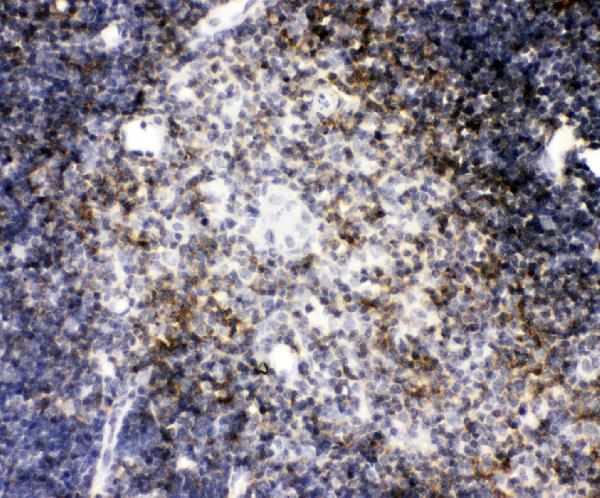
AFP levels in the membranes are used to measure the loss of kidney protein to the screen for spina bifida and anencephaly. A high level of AFP serum has been identified in patients with hepatocellular (HCC) carcinoma (HCC), terroatstastoma, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and germ cell neoplasms.
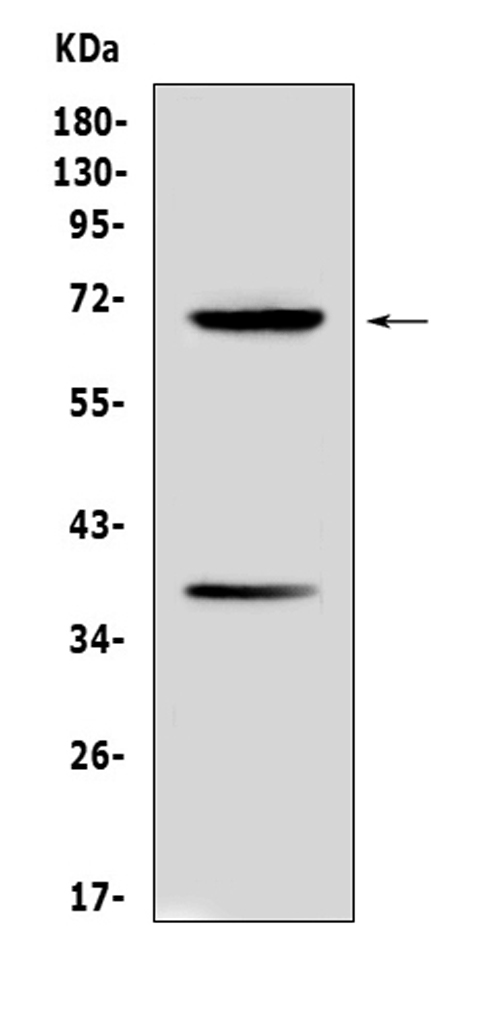
Anti-AFP antibodies are offered by a number of suppliers. This target gene encodes ‘alpha fetoprotein’ protein in humans and can also be known as Alpha-1-Fetoprotein, AFPD, Feta, HPAFP, and Alpha-Feto Globulin. Structurally, proteins reported 68.7 kilodalton in the masses, with subcellular localization issued.
AFP is famous for being the most abundant plasma protein in the human fetus, and to be biomarkers in certain tumors. Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) is 65 KDA glycoprotein found in the heart of the mammalian fetus, egg yolk bag, and GI channel. While AFP expression in adult cells is low, it is very stated in adult liver cancer cells.